

Duty Cycle - Working regimes in electric motors
(S1): Permanently working with constant load (Continuous duty)
The electric motor keeps a stable and constant temperature under rated load. Electromotor with duty cycle (S1) works continuously, without its temperature exceeding the allowable temperature.
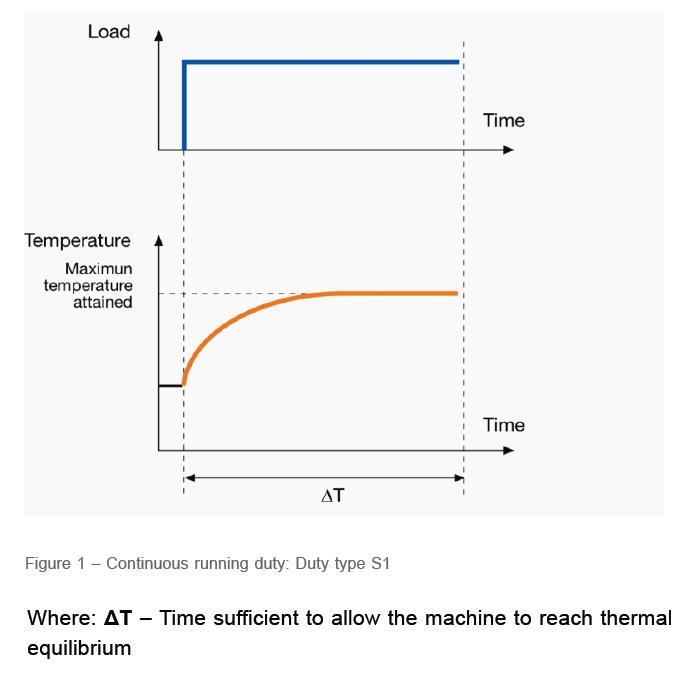
(S2): Working with a constant load in a short time (Short time duty)
The electric motor works in a short period with a nominal load. In this duty cycle category or (ΔT-C) should be shorter than the stop period and temperature loss. Intervals of 10, 30, 60, and 90 minutes are recommended for working time.
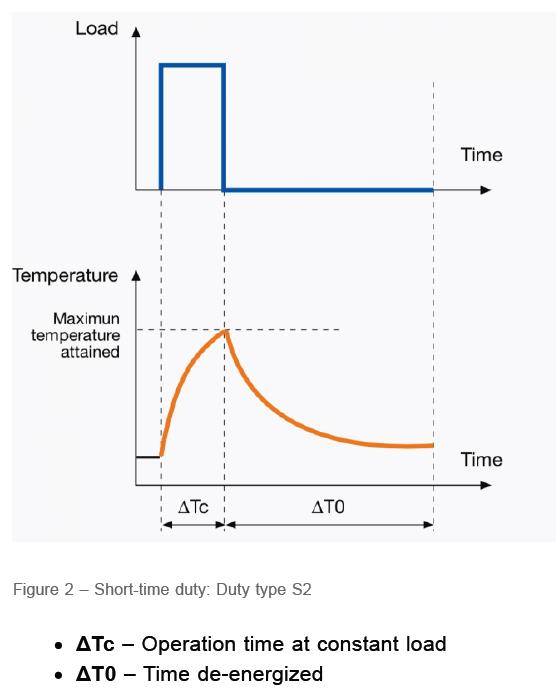
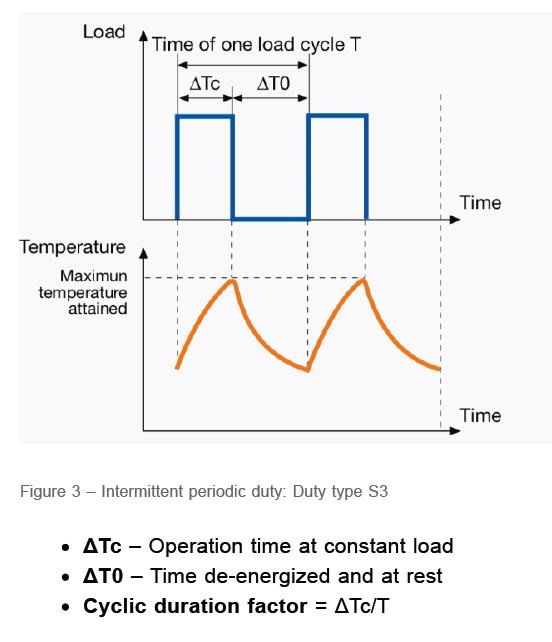
(S3): Intermittent periodic duty
In this category, the electric motor has a working and stop range as a percentage. It should be noted that in (S3) mode, the effect of starting and stopping current on the temperature rise of the electric motor is negligible. Recommended values for electric motor working cycle are equal to 15, 25, 40 and 60 percent.
(S4): Intermittent periodic duty with starting
In this category, the electric motor has a heavy starting cycle, operating at rated load and stopping. You can see these items in the sections (ΔTc), (ΔT*)) and (ΔT0) of the image below. The electric motor in this category is stopped by the force of the load or mechanical brakes, and its stopping process does not affect the temperature increase of the coils.

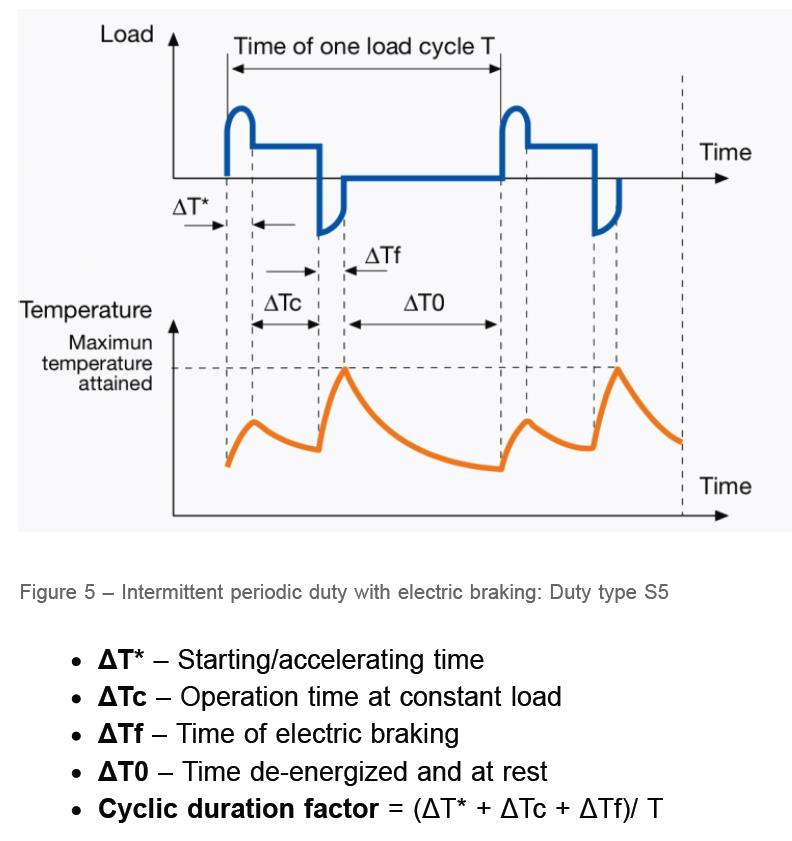
(S5): Intermittent periodic duty with starting and breaking
In this category, the electric motor has a heavy starting cycle, working with rated load and stopping with electronic brake. In simpler words, in class (S5) in addition to working with rated power, the effect of starting and stopping with electronic brake is also taken into account on the temperature increase of the coils.
(S6): Regular periodic continuous operation: (Continuous duty with Intermittent periodic loading)
In this class, the electric motor is always on, but its working range is defined as full load (ΔT-C) and without load (0-T). In other words, the electric motor in this class will not work with rated load. The recommended values for a 10-minute work interval are 15, 25, 40, and 60 percent.
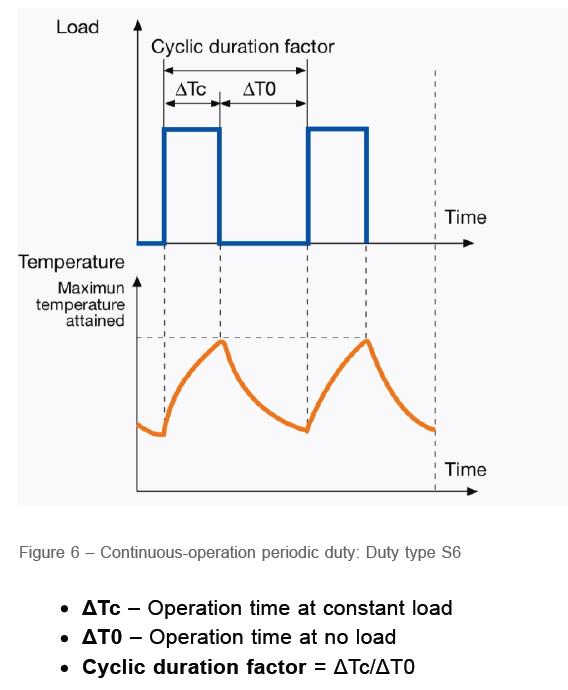
(S7): Continuous duty with starting and breaking
In this category, the electric motor is always working in a cycle that is repeated in the form of start-up, working with nominal load and electronic braking. Electronic brake in this group is considered as reverse flow. Since the electric motor in category (S7) never stops, the moment of inertia of the motor and the load be used to express its working period.
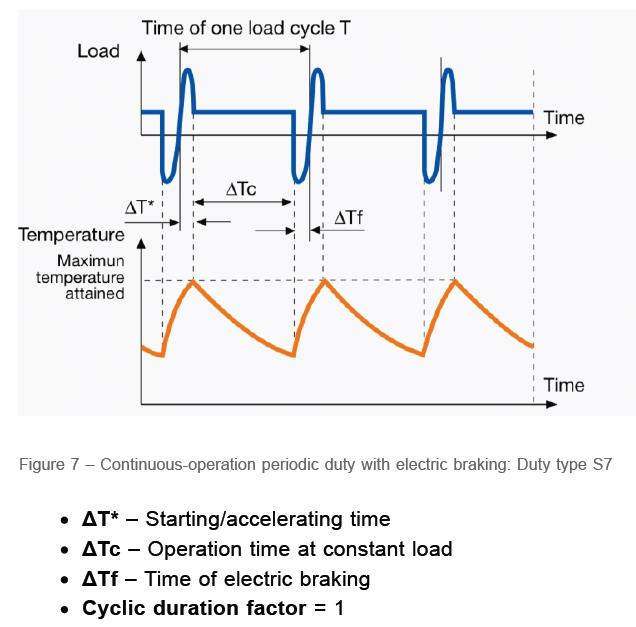
(S8): Continuous duty with periodic speed changes with related predicted load: (Continuous duty with periodic speed /load changes)
In this category, the electric motor works continuously and the cycles of start-up, speed change and electronic braking are repeated without stopping. The speed selection in this electric motor is done by changing the number of poles and the load has a constant value at each speed. For example, we can mention the speed change in Dahlander electric motors. You can see the working cycle of the electric motor in the (S8) category in the picture below. According to the picture, each working cycle includes starting, working and stopping at three different speeds. The load of the electric motor at each speed has a specific value, and the electronic brake is used before changing the poles of the electric motor.
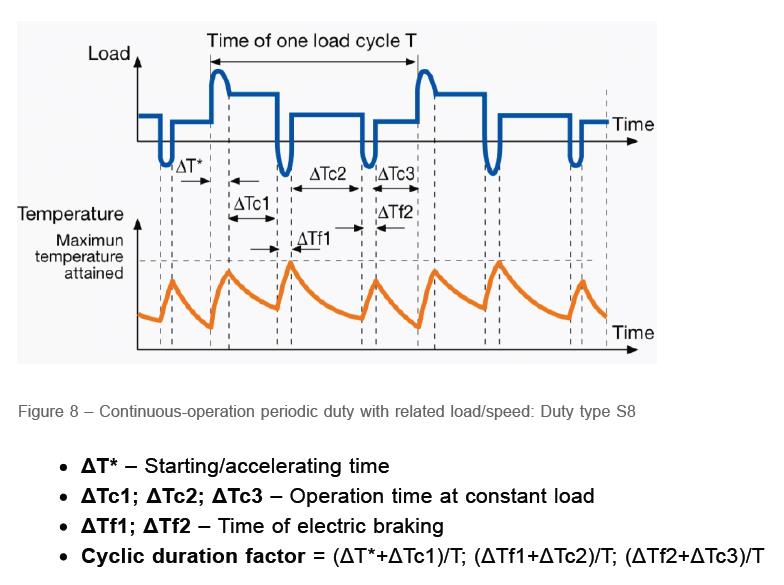
(S9): duty with non -periodic variations of speed and load
In this category, the amount of load and speed of the electric motor changes irregularly. In other words, in this mode, there is no regular cycle of starting, working, stopping, speed changing, etc. Changes in the load and speed of the electric motor are carried out within the permissible limits, but overload may also occur at moments. According to the picture below, in this working cycle, the amount of full load and overload is well-thought-out.
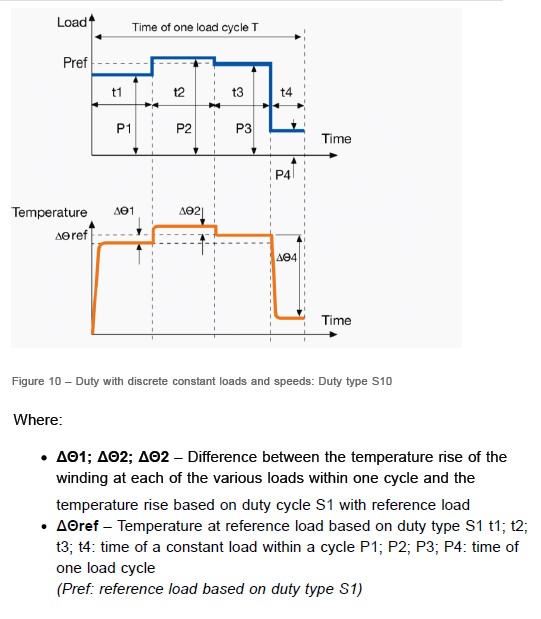
(S10): Duty with discrete constant loads and speeds
In this category, there are a certain number of separate loads and, if possible, different speeds. In the case of (S10), the loads and times have different values. For example, the electric motor can work without load for a certain period of time or it can be loaded to such an extent that the electric motor reaches equilibrium with the allowed temperature. The maximum load cannot exceed 1.15 times of S1 category
It should be mentioned that in the working periods (S3) to (S8), the electric motor operation time is generally much shorter than the time required to reach the heat exchange and equilibrium of the electric motor. The electric motor heats up alternately and cools down in each work cycle. Only after a large number of times of electric motor operation in work cycles (S3) to (S8) the electromotor reaches equilibrium and heat exchange.
To send comments, first fill the form and then send.
Factory
Address: Roshd Sanat Niroo Company, 21st South Street, Hashtgerd Industrial City
Email: factory@roshdsanatniroo.com
Phone: +98 49052, +982644226107
Fax: +982644220260
Central office
Address: No. 23, Shahid Akbari St., 22 Bahman St., Ashrafi Esfahani Highway, Tehran
Email: headoffice@roshdsanatniroo.com
Phone: +98 49052, +982148000981
Fax: +982144424892
All rights belong to Roshd Sanat Niroo Company.